# Attributed Strings
# Introduction
This topic discusses how to use attributed strings on the Android and iOS platform. You can manage and apply specific attributes, such as font and kerning, to characters or range of characters in a string used as the label text, text area value, or text field hint text or value. This feature is exposed using the Titanium.UI.AttributedString class.
# Creating an attributed string
To create an attributed string, use the Titanium.UI.createAttributedString method to create an AttributedString object by passing in a dictionary object that specifies the text and attributes properties:
The
textproperty specifies the text to use.The
attributesproperty specifies an array of attribute dictionaries to apply to the text. An attribute dictionary includes the following properties:type: the text attribute to apply as aTitanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_*constant.value: specifies a setting based on thetypeproperty, such as a color for a color attribute or dash style for a strikethrough or underline attribute.range: which characters to modify as an array range:[start_position, length].
After you have created your AttributedString object, to use it, set the attributedString property for either a Label, TextArea or TextField object.
Setting this property on a Label is equivalent to setting the
textproperty.Setting this property on a TextArea is equivalent to setting the
valueproperty.Setting this property on a TextField is equivalent to setting the
valueproperty.
You can also assign the AttributedString object to TextField's attributedHintText property, which is equivalent to setting the hintText property.
⚠️ Warning
If you use the attributedString or the attributedHintText property, do not set any other properties that modify the appearance of text, such as font, color, etc. If you use an attributed string, only use an attributed string. Titanium does not support using attributed strings with other text modifying properties.
The example below highlights the word "hyperloop" in the Label.
app.js
var win = Ti.UI.createWindow({
backgroundColor: '#ddd',
});
var text = "Have you tried hyperloop yet?";
var attr = Ti.UI.createAttributedString({
text: text,
attributes: [
{
type: Ti.UI.ATTRIBUTE_BACKGROUND_COLOR,
value: "yellow",
range: [text.indexOf('hyperloop'), ('hyperloop').length]
}
]
});
var label = Ti.UI.createLabel({
attributedString: attr
});
win.add(label);
win.open();
# Types of attributes
# Font
To specify a different font for part of your string, in the attribute dictionary, set the type property to Titanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_FONT and the value property to a custom Font dictionary to describe the font attributes.
var text = "Have you tried hyperloop yet?";
var attr = Ti.UI.createAttributedString({
text: text,
attributes: [
{
type: Ti.UI.ATTRIBUTE_FONT,
value: { fontSize: 24, fontFamily: 'Didot' },
range: [text.indexOf('hyperloop'), ('hyperloop').length]
}
]
});
# Foreground color
To specify a different text color for part of your string, in the attribute dictionary, set the type property to Titanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_FOREGROUND_COLOR and the value property to a color name or hex value.
var text = "Have you tried hyperloop yet?";
var attr = Ti.UI.createAttributedString({
text: text,
attributes: [
{
type: Ti.UI.ATTRIBUTE_FOREGROUND_COLOR,
value: 'cyan',
range: [text.indexOf('hyperloop'), ('hyperloop').length]
}
]
});
# Background color
To specify a different background color for part of your string, in the attribute dictionary, set the type property to Titanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_BACKGROUND_COLOR and the value property to a color name or hex value.
var text = "Have you tried hyperloop yet?";
var attr = Ti.UI.createAttributedString({
text: text,
attributes: [
{
type: Ti.UI.ATTRIBUTE_BACKGROUND_COLOR,
value: "yellow",
range: [text.indexOf('hyperloop'), ('hyperloop').length]
}
]
});
# Underline
To place a horizontal line under part of your string, set the type property to Titanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_UNDERLINES_STYLE.
For Android, you do not need to specify the value property. If set, the property is ignored by Android. Android only displays a single line under the text.
For iOS, set the value property to a Titanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_UNDERLINE_* constant describing the style of the horizontal line:
Titanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_UNDERLINE_STYLE_NONE: does not draw a lineTitanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_UNDERLINE_STYLE_SINGLE:draws a single line
Supported on iOS 7 and later:
Titanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_UNDERLINE_STYLE_THICK:draws a think lineTitanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_UNDERLINE_STYLE_DOUBLE:draws two linesTitanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_UNDERLINE_PATTERN_SOLID:draws a solid lineTitanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_UNDERLINE_PATTERN_DOT:draws a dotted lineTitanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_UNDERLINE_PATTERN_DASH:draws a dashed lineTitanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_UNDERLINE_PATTERN_DASH_DOT:draws an alternating dash and dot lineTitanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_UNDERLINE_PATTERN_DASH_DOT_DOT:draws an alternating dash and two dot lineTitanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_UNDERLINE_BY_WORD:draw lines only under or through characters
You can logically-OR more than one constant together to use more than one style or pattern.
For iOS 7 and later, you can control the color of the horizontal line. Set the type property to Titanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_UNDERLINE_COLOR and the value property to a color name or hex value.
var text = "Have you tried hyperloop yet?";
var attr = Ti.UI.createAttributedString({
text: text,
attributes: [
{
type: Ti.UI.ATTRIBUTE_UNDERLINES_STYLE,
value: Ti.UI.ATTRIBUTE_UNDERLINE_STYLE_DOUBLE | Ti.UI.ATTRIBUTE_UNDERLINE_PATTERN_DOT, // Ignored by Android only displays a single line
range: [text.indexOf('hyperloop'), ('hyperloop').length]
}
]
});
# Strikethrough
To place a horizontal line through part of your string, set the type property to Titanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_STRIKETHROUGH_STYLE.
For Android, you do not need to specify the value property. If set, the property is ignored by Android. Android only displays a single line through the text.
For iOS, set the value property to a Titanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_UNDERLINE_* constant describing the style of the horizontal line. See the previous section for a description of these constants. You can logically-OR more than one constant together to use more than one style or pattern.
For iOS 7 and later, you can control the color of the horizontal line. Set the type property to Titanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_STRIKETHROUGH_COLOR and the value property to a color name or hex value.
var text = "Have you tried hyperloop ti.next yet?";
var attr = Ti.UI.createAttributedString({
text: text,
attributes: [
{
type: Ti.UI.ATTRIBUTE_STRIKETHROUGH_STYLE,
value: Ti.UI.ATTRIBUTE_UNDERLINE_STYLE_THICK, // Ignored by Android only displays a single line
range: [text.indexOf('hyperloop'), ('hyperloop').length]
}
]
});
# Links
To add a link to part of your string, in the attribute dictionary, set the type property to Titanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_LINK and the value property to the URL. For iOS, this API only works on iOS 7 and later.
Listen for the link event to respond to a tap on linked text. Prior to Release 4.0, on iOS, the link event was only triggered by a long press.

var win = Ti.UI.createWindow({
backgroundColor: '#ddd',
});
var text = "Have your tried hyperloop yet?";
var attr = Ti.UI.createAttributedString({
text: text,
attributes: [
{
type: Titanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_LINK,
value: "https://github.com/tidev/hyperloop",
range: [text.indexOf('hyperloop'), ('hyperloop').length]
}
]
});
var label = Ti.UI.createLabel({
attributedString: attr
});
// Only works for iOS
label.addEventListener('link', function(e){
Ti.API.info(JSON.stringify(e));
});
win.add(label);
win.open();
# iOS attributes
The following attributes are only available on the iOS platform.
# Ligature
A ligature combines two or more characters in to a special character. To enable ligatures for your string, set the type property to Titanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_LIGATURE and the value property to 1 to use default ligatures. Set value to 0 to disable ligatures. Note that not all fonts support ligatures. Notice the difference between 'fi' when ligatures are disabled and enabled.
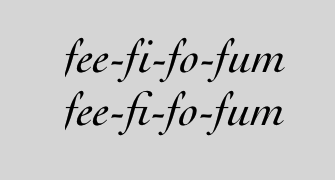
var text = "fee-fi-fo-fum\nfee-fi-fo-fum";
var attr = Ti.UI.createAttributedString({
text: text,
attributes: [
{
type: Ti.UI.ATTRIBUTE_FONT,
value: { fontSize: 24, fontFamily: Cochin-Italic' },
range: [0, text.length]
},
{
type: Titanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_LIGATURE,
value: 0,
range: [4, 1]
}
]
});
# Kerning
Kerning adjusts the spacing between characters. To specify a different kerning for part of your string, set the type property to Titanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_KERN and the value property to a float value specifying the distance between characters in points. Setting the value to 0 disables kerning, which is the default behavior.
var text = "Have you tried hyperloop yet?";
var attr = Ti.UI.createAttributedString({
text: text,
attributes: [
{
type: Ti.UI.ATTRIBUTE_KERN,
value: 5.0,
range: [text.indexOf('hyperloop'), ('hyperloop').length]
}
]
});
# Stroke text
To use a stroke text for part of your string, in the attribute dictionary, set the type property to Titanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_STROKE_WIDTH and the value property to a float describing the size of the outline. A positive value only displays an outline of the character, while a negative value fills the character.
To change the color of the text, set the type property to Titanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_STROKE_COLOR and the value property to a color name or hex value.

var text = "Have you tried hyperloop yet?";
var attr = Ti.UI.createAttributedString({
text: text,
attributes: [
{
type: Ti.UI.ATTRIBUTE_STROKE_COLOR,
value: 'red',
range: [text.indexOf('hyperloop'), ('hyperloop').length]
},
{
type: Ti.UI.ATTRIBUTE_STROKE_WIDTH,
value: 3.0,
range: [text.indexOf('hyperloop'), ('hyperloop').length]
}
]
});
# Shadow
To add a shadow effect to part of your string, in the attribute dictionary, set the type property to Titanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_SHADOW and the value property to a dictionary describing the shadow with the following properties:
blurRadius(iOS 7 and later): specifies the blur radius of the shadow.0means no blur.color: color name or hex triplet specifying the color of the shadow.offset: dictionary with the propertieswidthandheightused as the horizontal and vertical offset of the shadow, respectively.

var text = "Have you tried hyperloop yet?";
var attr = Ti.UI.createAttributedString({
text: text,
attributes: [
{
type: Ti.UI.ATTRIBUTE_SHADOW,
value: {color: 'green', offset: {width: 10, height: 5}},
range: [0, text.length]
}
]
});
# Letterpress effect
Supported on iOS 7 and later.
To add a letterpress effect to your text, in the attribute dictionary, set the type property to Titanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_TEXT_EFFECT and the value property to Titanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_LETTERPRESS_STYLE.

var text = "Have you tried hyperloop yet?";
var attr = Ti.UI.createAttributedString({
text: text,
attributes: [
{
type: Ti.UI.ATTRIBUTE_TEXT_EFFECT,
value: Ti.UI.ATTRIBUTE_LETTERPRESS_STYLE,
range: [text.indexOf('hyperloop'), ('hyperloop').length]
}
});
# Text direction
Supported on iOS 7 and later.
To change the direction of part of your string, in the attribute dictionary, set the type property to Titanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_WRITING_DIRECTION and the value property to a Titanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_WRITING_* constant:
Titanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_WRITING_DIRECTION_NATURAL: use the Unicode Bidirection Algorithm rules P2 and P3 (opens new window) to determine which direction to useTitanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_WRITING_DIRECTION_LEFT_TO_RIGHT: write the text from left to rightTitanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_WRITING_DIRECTION_RIGHT_TO_LEFT: write the text from right to left
You can logically-OR the previous writing direction constants with one of the below constants to specify the writing direction behavior:
Titanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_WRITING_DIRECTION_EMBEDDING: use the embedded direction of the textTitanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_WRITING_DIRECTION_OVERRIDE: override the embedded direction of the text and force the direction
var text = "Have you tried hyperloop yet?";
var attr = Ti.UI.createAttributedString({
text: text,
attributes: [
{
type: Ti.UI.ATTRIBUTE_WRITING_DIRECTION,
value: Ti.UI.ATTRIBUTE_WRITING_DIRECTION_RIGHT_TO_LEFT | Ti.UI.ATTRIBUTE_WRITING_DIRECTION_OVERRIDE,
range: [text.indexOf('hyperloop'), ('hyperloop').length]
}
]
});
# Baseline
Supported on iOS 7 and later.
To change the baseline (vertical position) of part of your string, in the attribute dictionary, set the type property to Titanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_BASELINE_OFFSET and the value property to a number specifying how many pixels above (positive value) or below (negative value) the main baseline to position the text.
var text = "Have your tried hyperloop yet?";
var attr = Ti.UI.createAttributedString({
text: text,
attributes: [
{
type: Ti.UI.ATTRIBUTE_BASELINE_OFFSET,
value: 10,
range: [text.indexOf('hyperloop'), ('hyperloop').length]
}
]
});
# Oblique
Supported on iOS 7 and later.
To skew part of your string, in the attribute dictionary, set the type property to Titanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_OBLIQUENESS and the value property to a float indicating how much skew to apply to the text. A value of 0 indicates no skewing, which is the default behavior.
var text = "Have your tried hyperloop yet?";
var attr = Ti.UI.createAttributedString({
text: text,
attributes: [
{
type: Ti.UI.ATTRIBUTE_OBLIQUENESS,
value: 0.25,
range: [text.indexOf('hyperloop'), ('hyperloop').length]
}
]
});
# Stretch
Supported on iOS 7 and later.
To stretch part of your string horizontally but not vertically, in the attribute dictionary, set the type property to Titanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_EXPANSION and the value property to a float indicating the log of the expansion factor to be applied. A value of 0 indicates no expansion, which is the default behavior.

var text = "Have your tried hyperloop yet?";
var attr = Ti.UI.createAttributedString({
text: text,
attributes: [
{
type: Titanium.UI.ATTRIBUTE_EXPANSION,
value: 0.25,
range: [text.indexOf('hyperloop'), ('hyperloop').length]
}
]
});