# Internationalization
# Objective
In this section, you will learn how you can seamlessly internationalize your Titanium apps. We'll look specifically at how you can use external language files to display text in the user's preferred language.
# Contents
Titanium provides a number of JavaScript functions in the Titanium.Locale namespace for use in localization. It also provides String formatting functions to handle dates, times, currencies, and more. You can even internationalize the name of your app itself. We'll look at those features, as well as how to test your language settings in this section.
# Language strings
Rather than hard-coding strings into your project, you can use localized strings. Localized strings are replaced at runtime with values appropriate to the user's language. Titanium relies on resources files and string placeholders to accomplish this task.
In your Alloy project create a directory called i18n. Inside the i18n folder, create folders for each language your application will support. Name the folder according to the ISO 639-1 (opens new window) standard. For example, use en for English, es for Spanish, fr for French, etc.
You can also add a suffix to the language directories for variants of languages. However, if you don't plan on adding multiple suffix-ed directories omit the suffix completely. Suffix the folder name with a dash followed by the country's ISO 3166-1 (opens new window) Alpha-2 code. For example, use en-US for American English, en-CA for Canadian English, en-GB for British English, etc. Note that the OS may not support all regional languages.
app
├── controllers
├── i18n
│ ├── en-AU
│ │ └── strings.xml
│ ├── en-CA
│ │ └── strings.xml
│ ├── en-GB
│ │ └── strings.xml
│ ├── en-US
│ │ └── strings.xml
│ └── fr
│ └── strings.xml
├── styles
└── views
⚠️ Warning
Titanium Classic Project Note
For Titanium classic projects you should put the i18n directory inside the root of your project (which is the same level as tiapp.xml file), not in the app directory.
# Resource file structure
The string resource file closely mirrors the format of Android localization files, which have an XML-based format. The name attribute represents the key for the string, and the text inside the XML node represents the value. A typical strings.xml file would look like the following:
strings.xml
<resources>
<string name="welcome_message">Welcome to Kitchen Sink for Titanium</string>
<string name="user_agent_message">user agent set to</string>
<string name="format_test">Your name is %s</string>
<string name="base_ui_title">Base UI</string>
<string name="controls_win_title">Controls</string>
<string name="phone_win_title">Phone</string>
<string name="platform_win_title">Platform</string>
<string name="mashups_win_title">Mashups</string>
<string name="ordered">Hi %1$s, my name is %2$s</string>
</resources>
Resource files are processed and included with your application at build time by our Titanium build scripts. This means that these strings won't be processed if you use Xcode or Eclipse to build your project natively.
⚠️ Warning
Android Platform Notes
If you have XML files in both the
i18nandplatform/androidfolders, the Titanium build scripts will try to merge the files together in thebuildfolder. If there are any conflicts, the build fails. Currently, if modules contain any files in theplatform/androidfolder, these files overwrite the build files.If you have strings using multiple substitutions, as demonstrated in the "ordered" string in the previous example, you may need to add the
formatted="false"attribute to these string elements if the localized string is not created correctly when running the application.When editing the strings.xml file, be sure to clean your project before building it again.
String resource names (the "keys") must begin with a letter and can contain digits, English characters, and the underscore. The contents (values) of each string resource must be UTF-8 (opens new window) compatible strings. While a given platform may not crash or throw an exception if you don't follow these rules, there's a good chance you will encounter some unexpected behavior.
# Getting a localized string
Titanium provides two functions for obtaining a localized string from your resource files. Both take the key of the string requested as their first parameter. The L() macro is a short form for Ti.Locale.getString() (opens new window):
var str1 = L('welcome_message');
var str2 = Ti.Locale.getString('welcome_message');
// str1 === str2
To handle situations where no key exists in the strings.xml file, the L() macro (opens new window) accepts a second argument to provide default hint text:
var str1 = L('missingKey', 'No translation available');
Additionally, you can use the titleid property of Titanium UI objects, such as labels or buttons, to directly reference a string resource without using the L() macro. For example:
var label = Ti.UI.createLabel({
titleid: 'welcome_message'
});
/*
* is equivalent to
* var label = Ti.UI.createLabel({
* text: L('welcome_message')
* });
*/
# Replacing values in a localized string
You probably noticed the %1 and %2 placeholders in the sample strings.xml file above. The String object in Titanium contains a format function which formats strings according to the IEEE printf specification (opens new window). If your localization string contains replacement keys, as format_test does in our example file above, you can replace values into your localized string like so:
var formatted = String.format(L('format_test'),'Kevin'); // contains 'Your name is Kevin'
Using the other replacement values from the printf spec, you can also do ordered values:
var formatted = String.format(L('ordered'), 'Jeff', 'Kevin'); // contains 'Hi Jeff, my name is Kevin'
# iOS-specific localizations
On iOS applications, you can localize the names of system buttons, such as "Save" and "Cancel", and the values of pList keys. You also need to modify the plist section of the tiapp.xml file in order to submit your application to international App Stores.
# Localize system buttons and submit to international App Stores
To localize system buttons or submit your application to international iTunes App Stores, add the CFBundleLocalizations key to the iOS plist section of the project's tiapp.xml file. Assign the CFBundleLocalizations key an array of strings. Each string is the ISO 639-1 standard name of the language you want the application to support. For example, to support English, Spanish and French, add the following to the application's tiapp.xml file:
tiapp.xml
<ti:app>
<ios>
<plist>
<dict>
<key>CFBundleLocalizations</key>
<array>
<string>en</string>
<string>fr</string>
<string>es</string>
</array>
</dict>
</plist>
</ios>
</ti:app>
# Localize property list keys
To localize property list key values (Info.plist keys), add string elements to the app.xml file with the name attribute set to the property list key and the node text to the localized string to display. For example, the following file provides French versions of several dialog messages displayed to the user when asking for permission to use their location, contacts or calendar.
i18n/fr/app.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<resources>
<string name="NSLocationAlwaysUsageDescription">Où allez-vous?</string>
<string name="NSContactsUsageDescription">Avez-vous des amis?</string>
<string name="NSCalendarsUsageDescription">Bon voyage.</string>
</resources>
# Set default language
The following key allows you to set the default language and region of your app which is very useful for the management of localization:
CFBundleDevelopmentRegion
<ios>
<plist>
<dict>
<key>CFBundleDevelopmentRegion</key>
<string>it_IT</string>
</dict>
</plist>
</ios>
For more information about CFBundleDevelopmentRegion, please review iOS Developer Library - Core Foundation Keys (opens new window) and iOS Developer Library - Language IDs (opens new window).
# Internationalizing the app's name
One thing that has been a little tricky for some developers, is changing the application name based on locale.
For example, say you had an application named "Cat", but you wanted it to be "Gato" in Spanish locales, "猫" in Japanese, and so on. Let 's see how you would prepare your application to display its name appropriately for both iOS and Android distributions.
# Changing locale for testing
Before learning to configure your apps to use localized strings for application names, let's first see how we can change locales manually for testing. Below you can find short videos for both iOS and Android that show you exactly how to do that.
Change Locale on iPhone (opens new window) from Appcelerator Video Channel (opens new window) on Vimeo (opens new window).
# App name localization
For iOS applications and if you are using Titanium SDK 3.2.0 and greater to build your Android applications, it's pretty simple. Use the standard method for creating localization paths, which means creating and using the i18n directory like this:
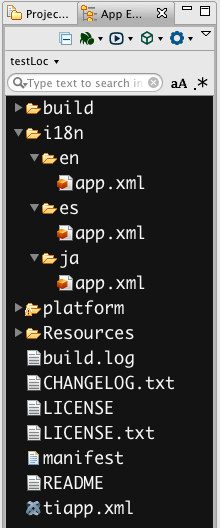
In each of your language directories under i18n, you'll include an app.xml file that includes the necessary XML structure for defining the localized name of your app. That structure will look like this for each file:
i18n/en/app.xml
<resources>
<string name="appname">Cat</string>
</resources>
i18n/es/app.xml
<resources>
<string name="appname">Gato</string>
</resources>
i18n/ja/app.xml
<resources>
<string name="appname">猫</string>
</resources>
And that's it. The next time you build your application, these localized strings will be used for your application name. If everything was configured correctly, you'll see the app name has changed based on the selected locale.
# Android app name localization with Titanium SDK 3.1.x and older
If you are using Titanium SDK 3.1.x and older to build your Android apps, the name localization is a little more involved. First, we need to create language-specific resource folders explicitly for Android. To do so, we will create the platform/android/res/values-(language code) directory structure, like this:
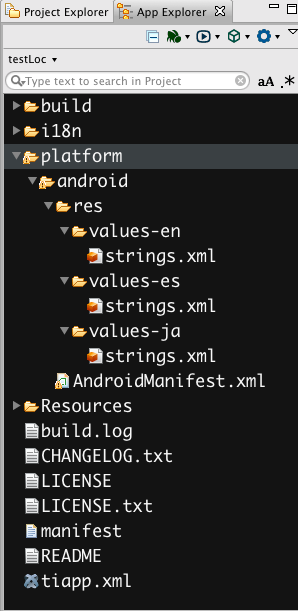
You'll notice in this case we are creating the Android native strings.xml files, rather than the app.xml files used by iOS. While the file names are different, the contents will be identical to those in the iOS files seen above.
Aside from the strings.xml files, there's one more thing we need to add. To make your app use these localized strings, you need to modify the existing AndroidManifest.xml. In order to do that, we need to add that custom manifest file, seen in the picture above at platform/android/AndroidManifest.xml. The AndroidManifest.xml file placed here should be a copy of the generated AndroidManifest.xml file found in your project's build/android directory. For more details on custom AndroidManifest.xml files, check out this wiki entry on the topic.
Now open up platform/android/AndroidManifest.xml and change the android:label attributes of the <application> and <activity> elements from the defined value of your app name to the value @string/app_name. Yeah, that was a lot of instructions all in one sentence, so here's an example to show you what I mean:
AndroidManifest.xml
<!-- ... -->
<!-- TI_MANIFEST -->
<application android:icon="@drawable/appicon"
android:label="@string/app_name" android:name="TestlocApplication"
android:debuggable="false">
<!-- TI_APPLICATION -->
<activity android:name=".TestlocActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" android:theme="@style/Theme.Titanium"
android:configChanges="keyboardHidden|orientation">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<!-- The rest of your AndroidManifest.xml -->
With these changes in place, you can now rebuild your app (probably best to give it a clean first) and you'll have a successfully localized application name.
# Reference
This is how your home screens might look on Android and iOS when Japanese is the selected language.
|
|
And just in case my description was clear as mud, check out a Titanium project with these localizations set up first hand. Just go to the AppNameLocalization project repository (opens new window) on Github. It contains the very basic project discussed here. With all this, you should be well-equipped to distribute your apps in as many languages as you wish to support.
# Links
Appcelerator Wiki: Maintaining a Custom AndroidManifest.xml
# Internationalizing image and file resources
Titanium does not provide built-in functions for internationalizing image and file resources. But you can easily accomplish this yourself. There are a couple of techniques you can employ:
Put the path and file name of each resource in the
strings.xmlfile, then use that string in theimageproperty, like this:var img = Ti.UI.createImageView({ image: L('my_image') });Put your images into a set of folders that match the 2-letter ISO codes, and include that directory in the path with
Ti.Locale.currentCountry, like this:var img = Ti.UI.createImageView({ image: 'images/'+Ti.Locale.currentCountry+'/my_image.png' });
⚠️ Warning
This technique won't work for the splash screen graphics. You should ideally avoid text that would need translation in your splash screen.
See Localized splash screens for more information.
# Date and time formatting
Titanium provides string formatting functions (opens new window) that you can use to create formatted dates and times. These include String.formatDate() and String.formatTime(). You can use these methods to format a JavaScript Date object to locale-specific strings.
At the time of this writing, natively, Android does not format dates in accordance with the official DateFormat (opens new window) documentation. Consequently, this will affect the corresponding short, medium and long formats of Titanium String Formatting. Furthermore, when the device settings are set to certain languages, the translations can be wrong or fields in the incorrect order. For example, the following code is run on a device to demonstrate the issue:
app.js
Ti.API.info("Ti.Locale.currentLanguage = " + Ti.Locale.currentLanguage);
Ti.API.info("Ti.Locale.currentLocale = " + Ti.Locale.currentLocale);
Ti.API.info("thisDate = " + thisDate);
Ti.API.info("thisDate short = " + String.formatDate(thisDate,"short"));
Ti.API.info("thisDate medium = " + String.formatDate(thisDate,"medium"));
Ti.API.info("thisDate long = " + String.formatDate(thisDate,"long"));
This results in the following when the device is set to display in Polish:
Log output (info)
TiAPI I (kroll$1: app://app.js) [4,603] Ti.Locale.currentLanguage = pl
TiAPI I (kroll$1: app://app.js) [3,606] Ti.Locale.currentLocale = pl-PL
TiAPI I (kroll$1: app://app.js) [7,613] thisDate = Mon May 23 2011 13:38:33 GMT-0000 (GMT+00:00)
TiAPI I (kroll$1: app://app.js) [6,619] thisDate short = 23-05-2011
TiAPI I (kroll$1: app://app.js) [6,625] thisDate medium = 23-05-2011
TiAPI I (kroll$1: app://app.js) [4,629] thisDate long = 23 maja 2011
Here, maja is output for the month of May, whereas the Polish for May is actually Maj.
Similarly, when the device is set to English (United Kingdom), the month fields are incorrectly displayed before the dates:
Log output (info)
TiAPI I (kroll$3: app://app.js) [2,1056] Ti.Locale.currentLanguage = en
TiAPI I (kroll$3: app://app.js) [1,1057] Ti.Locale.currentLocale = en-GB
TiAPI I (kroll$3: app://app.js) [9,1066] thisDate = Mon May 23 2011 14:09:28 GMT-0000 (GMT+00:00)
TiAPI I (kroll$3: app://app.js) [258,1324] thisDate short = 5/23/11
TiAPI I (kroll$3: app://app.js) [4,1328] thisDate medium = May 23, 2011
TiAPI I (kroll$3: app://app.js) [13,1341] thisDate long = May 23, 2011
This issue may well be fixed by the time you read this but, nevertheless, it gives us an opportunity to employ some of Titanium's tools to provide a workaround that gives you full control over the date format and translations.
We can use JavaScipt's Date (opens new window) object to return the date, which provides methods such as getDate() and getFullYear() to individually retrieve some of the information that we need. Although it does not specifically provide a method for returning the name of the month, we can derive it, in English, from the space-separated string output from Date. To do so, we'll use the JavaScipt String.split() (opens new window) function. This will give us a key to lookup in the string.xml files.
app.js
var thisDate = new Date(); // will always return date in English
Ti.API.info("Ti.Locale.currentLanguage = " + Ti.Locale.currentLanguage);
Ti.API.info("Ti.Locale.currentLocale = " + Ti.Locale.currentLocale);
Ti.API.info("thisDate = " + thisDate);
var thisMonth = thisDate.toString().split(' ',2)[1];
Ti.API.info("The month contained in thisDate is: " + thisMonth);
Ti.API.info("Note: as thisMonth is always in the default language, English, it can be used to look up the localized string.");
Ti.API.info("Hence, the localized string, headingDate, in the language of " + Ti.Locale.currentLanguage + " is:");
Ti.API.info(String.format(L('headingDate'),thisDate.getDate(),L(thisMonth),thisDate.getFullYear()));
Using string substitution placeholders, dynamic values can be passed to the headingDate string. This enables each locale to display the fields in a different order. In the following string.xml files, Polish and English translations will return the date in the default order, whereas Spanish will result in a modified order.
i18n/pl/strings.xml
<resources>
<string name="headingDate">%d %s %d</string>
<string name="January">Stycze?</string>
<string name="February">Luty</string>
<string name="March">Marzec</string>
<string name="April">Kwiecie?</string>
<string name="May">Maj</string>
<string name="June">Czerwiec</string>
<string name="July">Lipiec</string>
<string name="August">Sierpie?</string>
<string name="September">Wrzesie?</string>
<string name="October">Pa?dziernik</string>
<string name="November">Listopad</string>
<string name="December">Grudzie?</string>
</resources>
i18n/en/strings.xml
<resources>
<string name="headingDate">%d %s %d</string> // Note: reordered keys not working on Android. Issue under investigation
<string name="January">January</string>
<string name="February">February</string>
<string name="March">March</string>
<string name="April">April</string>
<string name="May">May</string>
<string name="June">June</string>
<string name="July">July</string>
<string name="August">August</string>
<string name="September">September</string>
<string name="October">October</string>
<string name="November">November</string>
<string name="December">December</string>
</resources>
i18n/es/strings.xml
<resources>
<string name="headingDate">%2$s %1$d, %3$d</string>
<string name="January">enero</string>
<string name="February">febrero</string>
<string name="March">marzo</string>
<string name="April">abril</string>
<string name="May">mayo</string>
<string name="June">junio</string>
<string name="July">julio</string>
<string name="August">agosto</string>
<string name="September">septiembre</string>
<string name="October">octubre</string>
<string name="November">noviembre</string>
<string name="December">diciembre</string>
</resources>
Using this code, the date in Polish is translated correctly:
Log output (info)
TiAPI I (kroll$3: app://app.js) [1,1366] Ti.Locale.currentLanguage = pl
TiAPI I (kroll$3: app://app.js) [1,1367] Ti.Locale.currentLocale = pl-PL
TiAPI I (kroll$3: app://app.js) [33,1400] thisDate = Mon May 23 2011 15:05:21 GMT-0000 (GMT+00:00)
TiAPI I (kroll$3: app://app.js) [38,1479] The month contained in thisDate is: May
TiAPI I (kroll$3: app://app.js) [1,1480] Note: as thisMonth is always in the default language, English, it can be used to look up the localized string.
TiAPI I (kroll$3: app://app.js) [12,1492] Hence, the localized string, headingDate, in the language of pl is:
TiAPI I (kroll$3: app://app.js) [18,1510] 23 Maj 2011
In addition, the recognized date format for the UK is produced:
Log output (info)
TiAPI I (kroll$1: app://app.js) [2,577] Ti.Locale.currentLanguage = en
TiAPI I (kroll$1: app://app.js) [2,579] Ti.Locale.currentLocale = en-GB
TiAPI I (kroll$1: app://app.js) [2094,2673] thisDate = Mon May 23 2011 14:56:42 GMT-0000 (GMT+00:00)
TiAPI I (kroll$1: app://app.js) [20,2707] The month contained in thisDate is: May
TiAPI I (kroll$1: app://app.js) [1,2708] Note: as thisMonth is always in the default language, English, it can be used to look up the localized string.
TiAPI I (kroll$1: app://app.js) [1,2709] Hence, the localized string, headingDate, in the language of en is:
TiAPI I (kroll$1: app://app.js) [13,2722] 23 May 2011
Lastly, the date in Spanish has been reordered:
Log output (info)
TiAPI I (kroll$5: app://app.js) [2,1066] Ti.Locale.currentLanguage = es
TiAPI I (kroll$5: app://app.js) [6,1072] Ti.Locale.currentLocale = es-US
TiAPI I (kroll$5: app://app.js) [169,1241] thisDate = Mon May 23 2011 16:23:17 GMT-0000 (GMT+00:00)
TiAPI I (kroll$5: app://app.js) [32,1440] The month contained in thisDate is: May
TiAPI I (kroll$5: app://app.js) [2,1442] Note: as thisMonth is always in the default language, English, it can be used to look up the localized string.
TiAPI I (kroll$5: app://app.js) [14,1456] Hence, the localized string, headingDate, in the language of es is:
TiAPI I (kroll$5: app://app.js) [14,1470] mayo 23, 2011
# Other formatting and locale functions
Titanium also provides string formatting functions that you can use to create formatted currency and decimal numbers. These functions are String.formatCurrency() and String.formatDecimal(), respectively. The Ti.Locale module (opens new window) provides the Ti.Locale.formatTelephoneNumber() method for getting a locale-formatted phone number. That module also includes functions for retrieving the correct currency symbol and currency code for the user's locale.
# Testing languages
When building internationalized apps, you'll need to test each of the supported languages. You can do so either on-device or in the simulator/emulator. In each case, you configure the device's language settings to change locales.
To set the language on iOS:,
Open Settings.
Tap General, then Language & Region.
Under iPhone Language, select the language to use, then tap Done.
iOS will ask you to confirm your changes. Tap Change to....
Optionally, in Settings, tap General, Language & Region, Region Format to specify your locale format for dates and times.
⚠️ Warning
Localization is broken on the iOS 8.1 simulator.
To set the language on Android:
Open Settings.
Tap Language & input.
Tap Language and select the language to use.
# Hands-on practice
# Goal
In this activity, you will create an internationalized app that outputs language-specific strings and test that in the simulator/emulator.
# Steps
Create a new Titanium SDK project named "Language Test" with an app ID of your choice.
Using your computer's file management tools, create an
i18ndirectory at the/appdirectory of your project. In that directory, create two directories:enandes.Within the
endirectory, create astrings.xmlfile following the format shown above. Add three key/value pairs:language = Language
test = Test
tab = Tab
In the
esdirectory, create a matching copy ofstrings.xmlexcept that the values should be as follows:language = Lengua
test = Prueba
tab = Lengüeta
In the
esdirectory, create anapp.xmlfile following the format shown above. Add the necessary key and value to specify "Lengua Prueba" as the translated version of the app's name. (This won't have any effect if you're building for Android.)In app.js, on tab 1, add the necessary code to output the internationalized "Language Test" string as the text of
label1.On tab 2, change the text of
label2to output today's date using theString.formatDate()method.For both tab 1 and tab 2, update the text to use the internationalized "tab" key plus the tab's number.
Build the app for the simulator/emulator. The label and tab text should output in English (unless your emulator is already set to output text in Spanish). Close the app.
Change the simulator/emulator's settings to display text in Spanish. Open the app. Label and tab text should now be in Spanish. On iOS, the app's icon should be labeled in Spanish as well.
# Summary
In this chapter, you learned how to internationalize your app, including using language strings, internationalizing the app name, and formatting strings, dates, and currency values.

